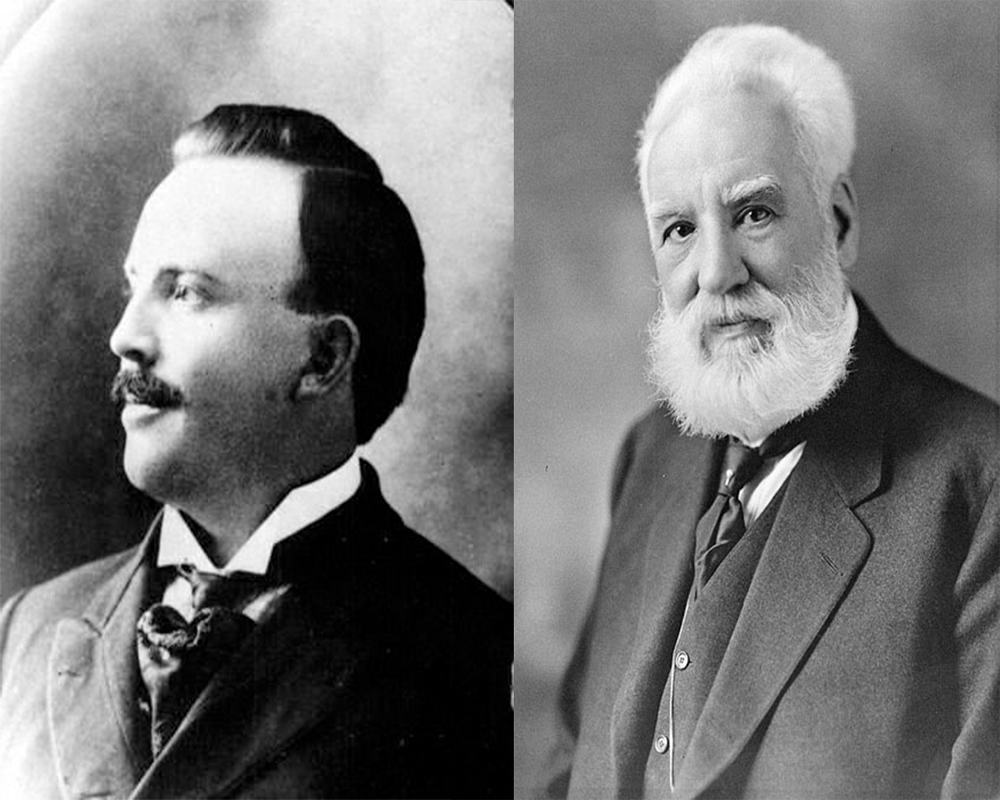| Basic Information | Alexander Graham Bell | Nathaniel Baldwin |
| Nationality | Canadian, United Kingdom (1847 – 1922), United Kingdom (1882 – 1922) | Canadian |
| Date of Birth | 3rd March 1847 | 1st December 1878 |
| Place of Birth | Edinburgh, Scotland | Fillmore, Millard County, Utah, Canada |
| Date of Death | 2nd August 1922 | 19th January 1961 |
| Place of Death | Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, Canada | Salt Lake City, Utah. |
| School | Royal High School, Edinburgh, Scotland | N / A |
| High School / College | N / A | N / A |
| University | The University of Edinburgh, University College London | N / A |
| Occupation | Inventor, Scientist, Engineer, Professor, Teacher of the deaf | The Baldwin Radio Company |
| Career | 1862 – 1922 | 1890 – 1961 |
| Famous for | The invention of the telephone | The inventor of Head Phones |
| Title | Inventor | Making Head Phones |
| Other works | Nail brushes for the Mill, American Asylum for Deaf-mutes, Photophone, Phonograph, selenium cells, Metal detector, Portrayal in film and television | The Baldwin Radio Company, Worked for the navy in World War I. |
| Awards | NAS Member in 1883 Albert Medal in 1902 John Fritz Medal in 1907 Elliott Cresson Medal in 1912 | N / A |
Alexander Graham Bell:
Alexander Graham Bell 3rd March 1847was a Scottish-conceived innovator, researcher, and architect who is credited with imagining and protecting the main down to earth phone. He additionally helped to establish the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885[1].

Chime’s dad, granddad, and sibling had all been related with chip away at rhetoric and discourse and the two his mom and spouse were hard of hearing, significantly impacting Bell’s all-consuming purpose[2].
Early Life and Family:
The second child of Alexander Melville Bell and Eliza Grace Symonds Bell, he was named for his fatherly granddad. The center name “Graham” was included when he was 10 years of age. He had two siblings, Melville James Bell and Edward Charles Bell, both of whom kicked the bucket from tuberculosis[2].
During his childhood, Bell was firmly impacted by his family and his environs. Bell’s old neighborhood of Edinburgh, Scotland, was known as the “Athens of the North” for its rich culture of expressions and science. His granddad and father were specialists in the mechanics of voice and rhetoric. Furthermore, Bell’s mom, Eliza, turned into a refined musician despite being hard of hearing, motivating him to embrace enormous difficulties. Eliza self-taught her child and ingrained a limitless interest in his general surroundings. He got one year of formal training in a non-public school and two years at Edinburgh’s acclaimed Royal High School[2].
Even though an unremarkable understudy, Bell showed an extraordinary capacity to take care of issues. At age 12, while playing with a companion in a grain factory, he saw the moderate cycle of husking the wheat grain. He returned home and constructed a gadget with pivoting oars and nail brushes that effectively eliminated the husks from the grain[2].

Early Career:
Youthful Alexander was prepared since early on to carry on in the privately-run company, however, his adamant nature clashed with his dad’s tyrannical way. Searching for an exit plan, Alexander elected to think about his granddad when he became sick in 1862. The senior Bell empowered youthful Alexander and imparted gratefulness for learning and scholarly interests. By age 16, Alexander had joined his dad in his work with the hard of hearing and before a long-expected full charge of his dad’s London tasks. [2]
On one of his excursions to North America, Alexander’s dad concluded it was a more beneficial climate and chose to move the family there. From the start, Alexander opposed, for he was setting up himself in London. He in the long run yielded after the two of his siblings passed on of tuberculosis. In 1870, the family got comfortable in Brantford, Ontario, Canada. There, Alexander set up a workshop to proceed with his investigation of the human voice[2].
On 11th July 1877, Bell wedded Mable Hubbard, a previous understudy and the little girl of Gardiner Hubbard, one of his initial monetary supporters. Mable had been hard of hearing since her youth years[2].
Alexander Graham Bell’s Inventions:
Chime is credited with creating the phone; on the whole, he by and by held 18 licenses alongside 12 he imparted to colleagues[2].
Work with Deaf:
Bell’s dad was welcomed by Sarah Fuller, head of the Boston School for Deaf Mutes (which proceeds with today as the public Horace Mann School for the Deaf), in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, to present the Visible Speech System by giving preparing to Fuller’s educators, yet he declined the post for his child. Making a trip to Boston in April 1871, Bell demonstrated fruitful in preparing the school’s instructors. He was consequently approached to rehash the program at the American Asylum for Deaf-quiets in Hartford, Connecticut, and the Clarke School for the Deaf in Northampton, Massachusetts[1].

Getting back to Brantford following a half year abroad, Bell proceeded with his tests with his “symphonious telegraph”. The essential idea of driving his gadget was that messages could be sent through a solitary wire if each message was communicated at an alternate pitch, yet chip away at both the transmitter and recipient was needed[1].
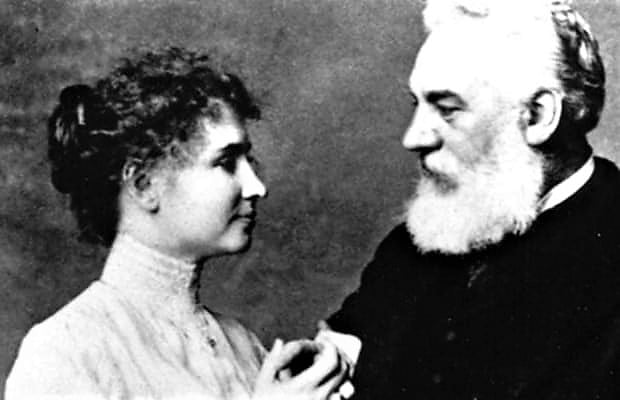
Uncertain of his future, he originally mulled over getting back to London to finish his investigations, however, chose to re-visitation Boston as a teacher. His dad helped him set up his private practice by reaching Gardiner Greene Hubbard, the leader of the Clarke School for the Deaf for a suggestion. Showing his dad’s framework, in October 1872, Alexander Bell opened his “School of Vocal Physiology and Mechanics of Speech” in Boston, which pulled in countless hard of hearing understudies, with his top-notch numbering 30 students. While he was functioning as a private mentor, one of his students was Helen Keller, who came to him as a small kid unfit to see, hear, or talk. She was later to state that Bell committed his life to the entrance of that “brutal quietness which isolates and estranges”. In 1893, Keller played out the turf breaking function for the development of Bell’s new Volta Bureau, devoted to “the expansion and dispersion of information identifying with the deaf”[1].
A few powerful individuals of the time, including Bell, seen deafness as something that ought to be killed and accepted that with assets and exertion, they could show the hard of hearing to understand lips and talk (known as oralism) and not utilize gesture-based communication, along these lines empowering their combination inside the more extensive society from which many were regularly being excluded. Owing to his endeavors to stifle the instructing of communication via gestures, Bell is frequently seen adversely by those grasping Deaf culture[1].
Somewhere in the range of 1873 and 1874, Bell spent long days and evenings attempting to consummate the symphonious message. In any case, during his tests, he got keen on another thought, communicating the human voice over wires. Chime’s redirection baffled his sponsors, and Thomas Watson, a gifted circuit tester, was recruited to pull together Bell on the consonant message. Yet, Watson before long got fascinated with Bell’s concept of voice transmission and the two made an incredible organization with Bell being the thought man and Watson having the ability to bring Bell’s plans to the real world[2].
‘Mr. Watson, come here – I want to see you’
Through 1874 and 1875, Bell and Watson worked on both the symphonious message and a voice sending gadget. Even though from the outset disappointed by the redirection, Bell’s financial specialists before long observed the estimation of voice transmission and recorded a patent on the thought[2].
Later Developments:
On 10th March 1876 Bell utilized “the instrument” in Boston to call Thomas Watson who was in another room however too far to hear. He stated, “Mr. Watson, come here – I need to see you” and Watson before long showed up at his side[1].

Proceeding with his trials in Brantford, Bell got back a working model of his phone. On August 3, 1876, from the message office in Brantford, Ontario, Bell sent a conditional wire to the town of Mount Pleasant four miles (six kilometers) far off, showing that he was prepared. He settled on a phone decision by means of transmit wires and weak voices were heard answering. The next night, he flabbergasted visitors just as his family with a call between the Bell Homestead and the workplace of the Dominion Telegraph Company in Brantford along an extemporized wire hung along transmit lines and fences, and laid through a passage. This time, visitors at the family unmistakably heard individuals in Brantford perusing and singing. The third test on August 10, 1876, was made by means of the message line among Brantford and Paris, Ontario, eight miles (thirteen kilometers) far off. This test was said by numerous sources to be the “world’s initially significant distance call”. The last test surely demonstrated that the phone could work over significant distances, at any rate as a single direction call[1].
Nathaniel Baldwin:
Baldwin was born on 1st December 1878 in Fillmore, Millard County, Utah to Nathaniel B. Baldwin, a local of Ontario, Canada, and Margaret Ohler, a local of Philadelphia. Baldwin’s family were individuals from The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and his mom was his dad’s second polygamous spouse. As a youngster, he was keen on innovation and manufactured his bike and steam motor[3].

Teaching:
Baldwin learned at Brigham Young Academy (BYA), Utah State Agricultural College, and afterward Stanford University, accepting a degree in electrical designing. He at that point got back to BYA to train in material science and religious philosophy and stayed after its name changed to Brigham Young University (BYU). Even though the LDS Church had formally suspended the act of polygamy in 1890, and again in 1904, individual educator John Tanner Clark persuaded Baldwin the congregation was committing an error. Since the LDS Church claimed BYU, this prompted Baldwin’s terminating and Clark’s banishment in 1905[3].
Designing and business:
“Nathaniel Baldwin Listen Up Here39s a Brief History of Headphones”
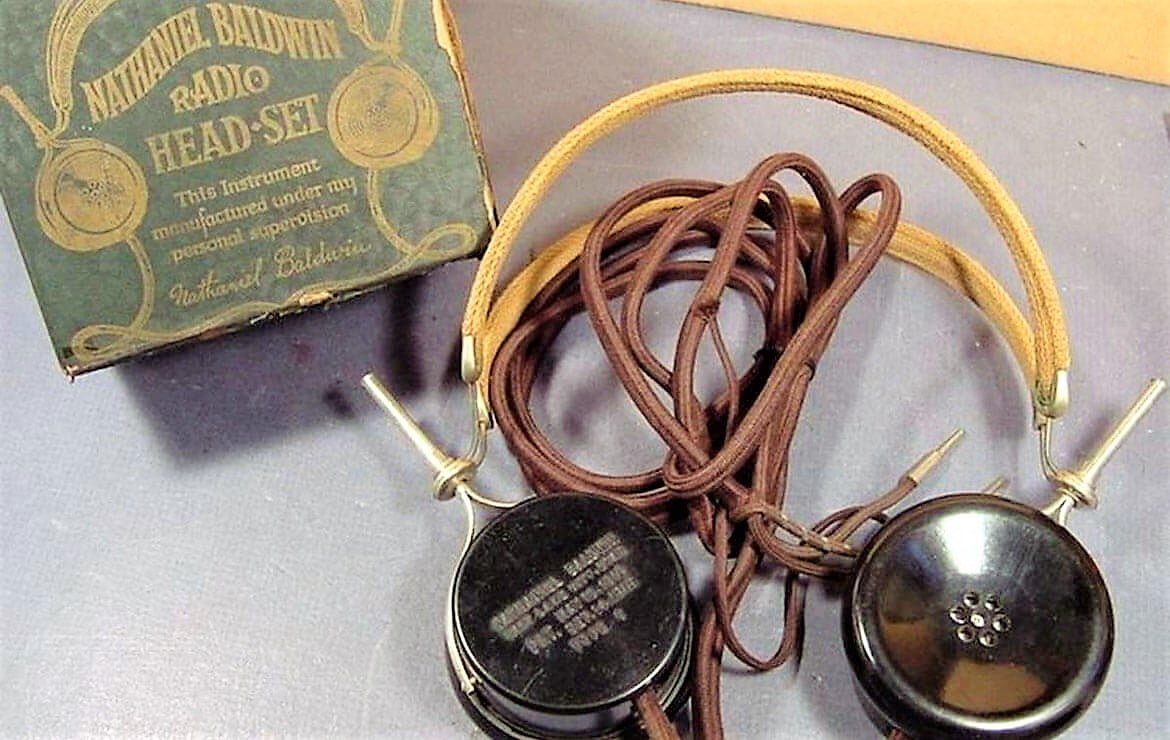
Baldwin at that point worked at far off hydroelectric plants at the Snake Creek close to Heber City and in East Mill Creek Canyon. He was additionally a circuit repairman and air blower administrator while he tried different things with sound enhancement utilizing compacted air. He utilized this to design more delicate collectors, which he made into the principal present-day earphones in 1910 and offered to the U.S. Naval force. His first ones were made by hand in quite a while kitchen and, despite the Navy’s proposal, never protected because he considered their innovation “trifling.”
In 1914, Baldwin began a business in East Millcreek, Utah called The Baldwin Radio Company. He fueled the plant and the area through a hydroelectric generator which he made out of bike haggles wire. The organization crested at 150 representatives and $2 million in yearly deals during the 1920s. One legend tells that Philo Farnsworth manufactured his first TV in Baldwin’s production line[3].
Baldwin utilized his prosperity to help uphold the post-Manifesto polygamous development during the 1920s. Numerous officials in his organization were driving polygamists, including Lorin C. Woolley, John Y. Barlow, Israel Barlow, Leslie Broadbent, and Lyman Jessop. During this time, these workers attracted up plans to make the Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints (FLDS Church) in southern Utah. He is considered the most significant money related help to the Mormon fundamentalist network before his organization fizzled[3].
Indiscreet speculations, frequently with individual allies of polygamy, prompted Baldwin’s organization’s liquidation in 1924. Omega Investment Company, which prompted his conviction of mail misrepresentation in 1930 and a two-year sentence at McNeil Island Federal Prison. After this period, Baldwin was always again unable to recover his past progress. Despite his doctrinal help of polygamy, he just wedded once, to Elizabeth Ann Butler. They were the guardians of seven youngsters[3].

The earphones were Perfected:
During the next years, the earphones experienced a broad development. The good being you don’t generally need to develop something new. It is similarly innovative to consummate a current development. In 1937 it was a German Bayer dynamic that made the DT-48 model of the main unique earphones for home tuning in. In 1949 the organization AKG from Vienna zeroed in on the plan while making the model K120[4].
Also, if Baldwin developed current earphones, it was John C. Koss, who is credited with making the principal sound system earphones Koss SP-3 out of 1958. He was a major Jazz sweetheart and his objective was to deliver earphones solely for tuning in to music[4].
1958: John C. Koss Introduces SP3 Stereo phones, Made for Music:
Until this point, individuals utilized earphones solely for radio correspondence. John Koss was brought up in Wisconsin. He got hitched in 1952, at which time he began a business utilizing a money wedding blessing with which he and his lady of the hour should purchase a couch, as indicated by the Wisconsin Historical Society[5].
While presenting a compact phonograph he needed to lease to patients in Milwaukee emergency clinics, he uncovered the first Koss SP3 stereo phones. At first, proposed to be a sidebar, the earphones demonstrated progressive because their sound quality made them ideal for tuning in to music. The Koss Corporation, situated in Milwaukee, is as yet making earphones today[5].
1979: Sony Releases ‘Walkman,’ Headphones Go on a Careful nutritional plan:
Before versatile music players, earphones would in general be large. Baldwin’s unique set gauged upwards of a pound. Koss’ stereo phones were circumoral, which means the earpads would in a real sense immerse your ears. It appeared well and good at that point. “Audiophiles” could tune in to the most recent Beatles, Pink Floyd, and Led Zeppelin collections in the solace of their homes, and the bulbous plan of their earphones assisted with hindering external clamor[5].

With the assistance of the Sony “Walkman,” recorded music before long freed itself from the home sound system, making a requirement for more convenient earphones. Helpfully, a lightweight arrangement of MDR-3L2 earphones was incorporated with the compact tape player. Instead of Koss’ circumoral earphones, Sony’s were supra-aural, which means the earpads squeezed against the ears[5].
1989: Dr. Amar Bose Introduces the First Noise-Reducing Headset:
On a flight home from Zurich in 1978, Dr. Amar Bose attempted an early arrangement of electronic earphones that were recently locally available for traveler diversion however, he could scarcely hear anything with the staggering lodge commotion. He got back to Boston and set up an examination program at Bose Corporation (which he established in 1964), to research how surrounding commotion could be decreased with dynamic clamor wiping out. The Noise Reduction Technology Group (NRTG) became out of that program, and in 1989, the organization presented the main commotion decrease headset, intended for the flight business[5].
2001: Apple iPod Includes Earbuds, Which Now Total 600 Million:
The pattern towards more modest and more convenient earphones, in the end, prompted earbuds and in-headphones, which just vary in how much they wedge into the ear channel[5].

In 2001, Apple acquainted the iPod with the world. The iPod, and later iPhone and iPad, accompanies a now-notorious arrangement of essential white earbuds. After 10 years, iPod deals have topped 300 million. Start to figure it out, adding up to deals of iPods, iPhones, and iPads, and you start to acknowledge there are a galactic number of Apple earbuds available for use. During the declaration of a hotly anticipated redesign of the organization’s stock headset at the iPhone 5 revealed on Sept. 12, Apple said that it had dispatched 600 million arrangements of the original of earbuds that is around one for every 12 individuals on the planet. Notwithstanding your conclusion on the nature of the item, those earbuds get around. [5]
2008: Beats by Dr. Dre Hits the Market:
Hip bounce craftsman and maker Dr. Dre collaborated with Interscope Chairman Jimmy Iovine to dispatch Beats by Dr. Dre, serving to set earphones as a style explanation. The brand has enrolled famous people, including Will.i.am, Justin Bieber, Lady Gaga, and Lebron James, to support the items. Today, beats by Dr. Dre have 63% piece of the overall industry in the U.S. for earphones evaluated over $100[5].
2011: Sennheiser Sells $40,000 Orpheus Headphones, World’s Most Expensive:
At a sound show in Seoul, South Korea, the German earphone organization Sennheiser divulged the world’s most costly earphones. The organization delivered 300 arrangements of the Orpheus earphones, which were evaluated at 30,000 Euros, or generally $41,000 apiece[5].
In case you’re as yet going back and forth about creation that large of speculation, give them a shot with the accompanying video[5].
2012: Apple Redefines Earbuds with the EarPods:
The dispatch of the iPhone 5 introduced another time of earphone plan the EarPods. The periscope-like earphones are intended to coordinate sound directly into the ear, and they hold up truly well. Earphones have made considerable progress in the previous 100 years, reforming how we burn-through media and how we convey. Notwithstanding sets that send with amazingly high devotion, other prominent progressions incorporate remote earphones, Bluetooth headsets, and headsets that incorporate a receiver that can be associated with phones or PCs. As compact media utilization keeps on ascending with cell phones and tablets, the requirement for earphones will be more noteworthy than at any other time[5].

What earphone enhancements do you expect throughout the following 100 years? What sort of earphones do jump at the chance to utilize? Increase the volume of this discussion in the remarks underneath[5].
if you want to check review about headphones then you can check Gadgetsquanta.com
References:
1. wikipedia. 23rd October 2020; Available from: wikipedia.
2. biography. 23rd October 2020; Available from: biography
3. alchetron. 23rd October 2020; Available from: alchetron
4. inventedfor. 23rd October 2020; Available from: inventedfor
5. mashable. 23rd October 2020; Available from: mashable.