| Basic Information | 1st Generation (1G) | 2nd Generation (2G) | 3rd Generation (3G) | 4th Generation (4G) | 5th Generation (5G) |
| Launched date | 1979 | 1991 | 1998 | 2008 | 2019 |
| First launched at the country | 1G technology was first time introduced in Tokyo, Japan | Finland with the GSM standard | Japan NTT DoCoMo for testing purposed and branded as FOMA | Stockholm and Oslo, Finland | South Korea |
| Introduced by company | NTT DoCoMo | Radiolinja (Now part of Elisa Oyj) | NTT DoCoMo | TeliaSonera | Swedish telecoms |
| Advancements in technology | New technology which bests for communications | GSM. GPRS, EDGE, SMS & MMS. Digital communication system | Video calling, mobile internet, | Improved the quality and signals | Not yet implement & main focus on the advance of 4G, Faster data rates, higher connection bulk, lower potential |
| Technology Type | Analog Technology | Digital technology | Digital technology (CDMA 2000 & TD-SCDMA) | Digital technology | Digital technology |
| Data transfer speed | 3-4kbp/sec | 110Kbp/sec | 2Mbps (for non-moving devices) & 384Kbps for moving devices like in a vehicle etc. | 200mbps | More than 1Gbps |
| Devices for the generation | Mobile phones are thick and bigger, low battery life | Mobile phone size reduced and battery life improved due to the digital transmission | Faster mobile devices, send and receive a large amount of data including videos. | Smart mobiles devices with efficient working like gaming services, HD mobile TV, Video conference, 3D TV and other services, moving device (in vehicles) 100mbp/s and non-moving devices 1Gbp/s | Smartphones arrived in the market, many companies like Samsung, Sony, OnePlus, Motorola, LG, and other companies are manufacturing these types of phones. |
| Drawback | Poor voice quality, Poor battery life, Large phone size, No security, Limited Capacity, Poor reliability | Required strong digitals signals for network coverage and digital signals weakened. Videos cannot be handled by the system. | Highly cost of upgrading base stations and cellular to 3G is very high, requires complex handsets, base stations need to be closer to each other, tremendous license costs, network deployment costs. | Limited Use of Internet and Smartphone, Battery Consumption, Limited 4G network towers, Cost of Phone, Higher data consumption | Obstacles can affect connectivity, Opening costs for the rollout are high, Restrictions of countryside contact, Battery-operated consuming on devices, Upload hurries don’t tie download speeds, Pessimistic from the esthetics |
1G Technology:
The 1G technology is also called as the “First Generation”. The wireless mobile communication was done only and only by the starter of 1G Technology. The first generation is also called since this technology was only used for the calls and it got the name of 1G that is widely used. Its very old technology and was used for the generations of mobile network technology. When 1G was launched, it was widely used by many peoples by the majority for many years. This was the 1st mobile technology that was used for mobile phones and utilized by the public. 1G Technology was launched in Tokyo, Japan by the company of DoCoMo. After it’s launched the 1G was widely spread in the country as well as Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Switzerland, Netherlands, Eastern Europe, and Russia, they had the standard of NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone) and these were basically on the 1G technology[1].
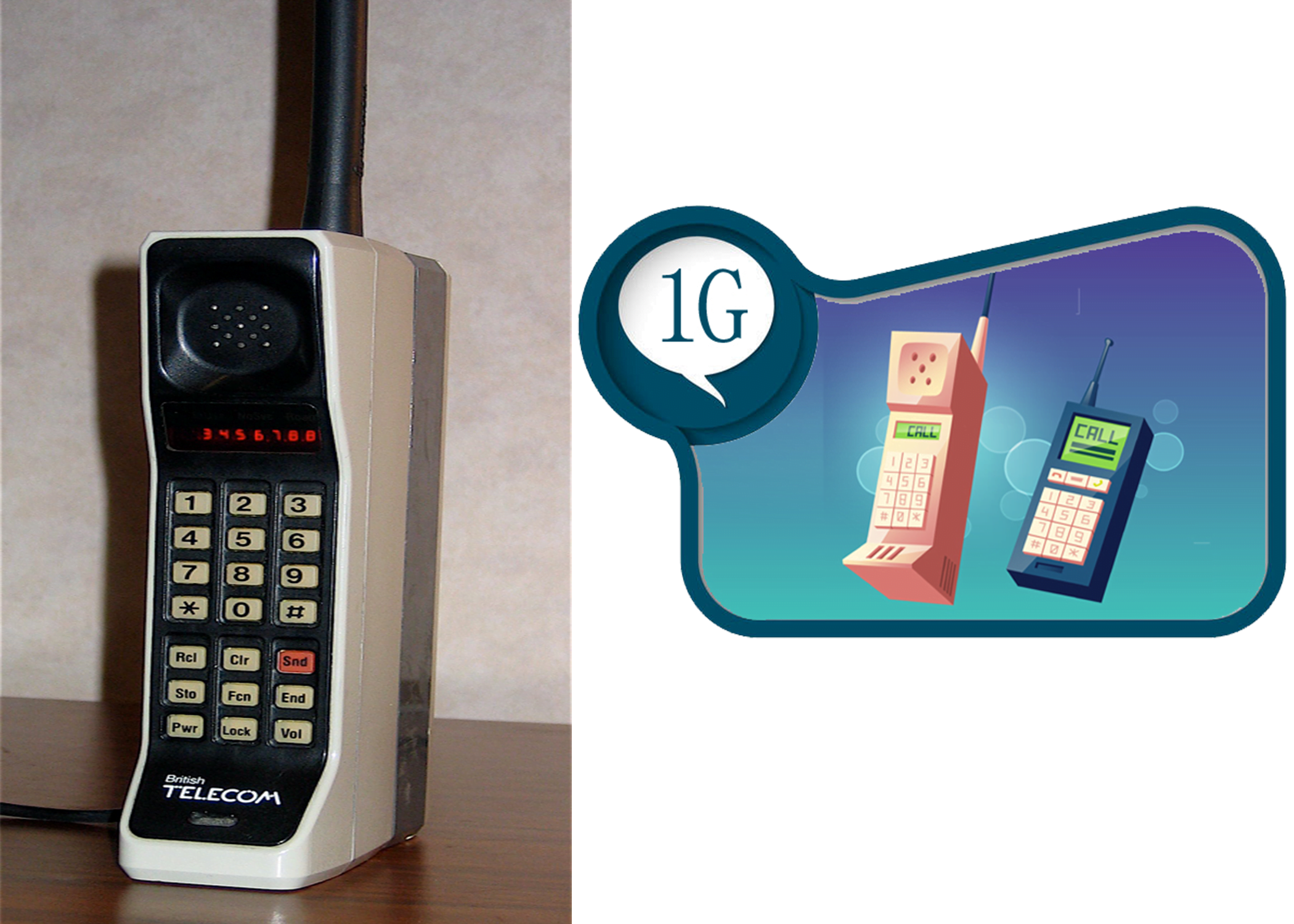

1G is an Analog technology that was widely used in the phones and had poor battery life and voice quality and also had no security features. 1G technology was the most experienced technology which was widely used all over the world and had a speed of 2.4 Kbp/sec. it was not fully digitalized and its data transmission in analog transmission was from 150Mhz and its above frequency was radio transmission waves which were the main drawback of 1G technology. Due to this, the phone calls were not secured and the data transmission was low and only calls and one-sided communication was possible. It had low data transmission speed at the time was around 3-4 Kbp/s and due to low frequency and analog form of data transmission, it consumed a lot of power of cell phone to send data to the distances and one thing which was disturbed while reaching the particular area the signals should be strong to reach that place. The mobile phones that were used at that time were bigger and heavy, difficult to carry them, roaming on the calls which takes a lot of battery in 1G technology, it means no calls to other countries. The 1G technology remained for 10 years of a long duration. After that 2G was launched[1].

Drawbacks of 1G technology[1]:
- Poor voice quality
- Poor battery life
- Large phone size
- No security
- Limited capacity
- Poor reliability
2G Technology:
2G or the Second generation of wireless technology was the technology which was introduced first in Finland in the year of 1991. 2G technology used digital signals for voice communication. It consumed the digital signals for the communication and this released a lot of improvements in the 1G technology and it becomes the different platform technology on the base of digitals signals and this gave us the content like picture messages at the low speed which was in Kbps. The bandwidth was used in the technology was about 30 to 200Khz. The introduction of 2G technology was in the early 90s, due to this the analog technology moved towards the digital World. In this technology, digital communication occurs in smaller devices, and secures the connection, supports better quality than 1G, and had a higher capacity for the connection[1].

This generation remained between the 90s and 2003 with very advancements made within the spectrum itself such as GSM, GPRS, and EDGE[1].
GSM: Stands for Global system for mobile communication which enables the transfer of voice communication with the speed of 30-35 kbps which is now a day to look like jokes. 2G technology played an important role in mobile phone connectivity and got famed[1].
GPRS: General Packet Radio Service which was operated on the similar 2G technology as GSM with the very few advancements which can give up to 110kbps[1].
EDGE: Enhanced data rates for GSM Evolution which was introduced in 2003 and this can be called the 2.9 or 3G due to the advancements over GPRS and GSM. Its speed is up to 135kbps and it continues to be used in many mobile networks[1].
2G: SMS and MMS[1]
- Mobiles/cellphones got their first significant update when they went from 1G to 2G. This jump occurred in 1991 on GSM networks first, in Finland, and adequately took mobile phones from simple to advanced.
- The 2G phone innovation presented call and text encryption, in addition to information administrations like SMS, picture messages, and MMS.
- The maximum speed of 2G with General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is 50 Kbps or 1 Mbps with Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE).

In 2G, three major highlights were added and improved contrasted with 1G and they are[1]:
1) Data transmission for telephone discussion got completely digitized and encoded.
2) Internet information administration and SMS like plain content, picture messages, MMS administration were started notwithstanding calls.
3) 2G empowered gadgets turned out to be more proficient to get and impart signs with higher infiltration levels for wide radio waves range.
Better voice quality, more than one medium to impart got another change remote correspondence innovation. With information encryption strategy, transmission turned out to be more proficient and quicker with better quality and information security. Just a specific beneficiary could get the proposed message through encryption strategy. The cell phone size likewise diminished somewhat. Battery life improved because of the digitization of information transmission which for the most part took less vitality to send. This occurred because of two diverse multiplexing principles on which 2G innovation depended on GSM (Global Systems for Mobile) given TDMA (Time Division Multiplexing Access) and CDMA (Code Division Multiplexing Access). This additional circuit exchanging space which permitted a solitary association progressively. On the off chance that the organization jumped from one base station to other base stations, at that point the association would in general disengage and everything must be re-started. Information transmission speed was additionally expanded to 14.4 kbps in contrast with 3-4 kbps in 1G[1].
Since simple segments were not, at this point required with the bounce to 2G, telephones could be made littler and more minimized, kicking off the pattern of ‘scaling down’. This is until we understood we could watch recordings on our telephones, at that point our telephone began going greater once more[1].
Drawbacks of 2G[1]:
- It required strong digital signals for the mobile phones working, network coverage, digital signals weakened.
- The videos cannot be handled by the system.
3G Technology:
The next generation is the 3G technology which was introduced in 1998 pre-commercially in Japan by the DoCoMo company for testing purposes and branded as FOMA. It was not released until 2001 and was officially released after 2003. The same year, the W-CDMA standard was commercially launched on GSM. At the same time, the European countries were using the UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication system) network with the standards of 3GPP[1].

More Data for internet and video calling[1]:
- 3G networks were introduced in 1998 and stand for the next generation in this series; the third-generation.
- 3G ushered in faster data-transmission speeds so you could use your cell phone in more data-demanding ways like for video calling and mobile internet. Like 2G, 3G evolved into 3.5G and 3.75G as more features were introduced to bring about 4G to date.
- The max speed of 3G was estimated to be around 2 Mbps for non-moving devices and 384 Kbps in moving vehicles. The theoretical max speed for HSPA+ is 21.6 Mbps.
This was a major insurgency as far as a mechanical progression for organization and information transmission. 3G had and has speed capacities of up to 2 Mbp/s. It empowered cell phones to give quicker correspondence, send/get enormous messages and messages, give quick web perusing, video real-time, and greater security among others. It was generally founded on CDMA2000 (Code-division different access) and EDGE advancements. Presently you may ask why EDGE? Indeed, because EDGE was so cutting-edge it had the option to give enough abilities to be considered as 3G. CDMA2000, then again, worked on comparative key ideas however improved. It empowered numerous channels to impart at one same subsequently extemporizing on the over speed and network[1].
The fundamental qualification somewhere in the range of 2G and 3G that permitted media spilling to occur is that 3G uses bundle exchanging information transmission as opposed to circuit exchanging. Information is separated into little pieces or bundles and afterward sent to the objective. Utilizing this strategy for transmission enormously speeds up, permitting one to send information through numerous directs in equal instead of one divert in an arrangement. This innovation likewise permits clients to pay for information utilized instead of time spent on the web[1].
Drawbacks of 3G technology[2]:
- Highly cost of upgrading base stations and cellular to 3G is very high,
- Requires complex handsets,
- Base stations need to be closer to each other,
- Tremendous license costs,
- Network deployment costs.
4G Technology:
In 2008, 4G innovation began to turn out yet had issues to monetarily declare the then correspondence framework as 4G because of the least standard prerequisites which were not satisfied. However, with headway in remote media transmission innovation, the least necessities for 4G innovation were practiced because of which specialists consented to call the current innovation 4G innovation. It satisfied the hole that was absent for more made sure about information transmission. All IP bundle switch network spaces are utilized for 4G consistency which implies all transmission depends on Internet Protocol. Here, information is given the most noteworthy need. The speed of the 3G network immediately got lacking as innovation and cell phones developed. The cutting edge came around 2010 out of two classifications 4G and 4G LTE (alluded to as just LTE). This age improved information moves speeds. 4G combability was about improved velocities as the answer for moderate information issues. 4G LTE had much quicker transfer speeds and was created dependent on IP guidelines. With speeds quicker than 3G, 4G transfer speed is 200mbp/s, which means the download time for a full-length film being around 10 minutes[1].
The Current Standard
The fourth era of organizations is called 4G. It upholds portable web access like 3G yet besides gaming administrations, HD versatile TV, Video Conferencing, 3D TV, and different administrations that request higher velocities. With the execution of 4G, some 3G highlights are taken out, for example, the range radio innovation; others are added to higher piece rates because of brilliant reception apparatuses. The most extreme speed of a 4G network when the gadget is moving is 100 Mbps or 1 Gbps for low versatility correspondence like when fixed or strolling. The 4G standard sets a few prerequisites for versatile organizations including ordering the utilization of Internet Protocol (IP) for information traffic and least information paces of 100 Mbps which was a colossal bounce from the 2 Mbps for 3G. It is regularly alluded to as MAGIC[1].
The term is used for explaining the 4G technology
M = Mobile multimedia
A = Any time anywhere
G = Global Mobility support
I = Integrated wireless solution
C = Customized Personal Service
4G LTE (Long Term Evolution) was delivered monetarily in December 2009 in the UK. It gave a top download speed of 100 Mbps and a highpoint transfer speed of 50Mbps. This empowered more information transmission simultaneously over the web convention. WiMAX was first delivered economically in June 2006 in South Korea which offered top information speed for download at 128 Mbps and pinnacle information speed for transfer at 56 Mbps[1].

“The 4G technology offers High-Quality video calls, teleconferencing with better quality and online gaming streams, secure and voice telephony, etc.”
Not long after 4G, 4G LTE was presented. LTE represents Long Term Evolution and it isn’t as much an innovation as it is the way followed to accomplish 4G speeds.4G VOLTE represents Voice Over Long-Term Evolution is an augmentation in LTE organization to completely digitize voice communication in parcel structure from circuit exchanged innovation. VOLTE can convey multiple times more information than the 3G UMTS organization and multiple times more information than the 2G GSM network[1].
5G Technology:
With 4G moving toward its cutoff points, you will likely hear the term 5G being tossed around a great deal, yet what is 5G? Indeed, 5G is the replacement to 4G portable organization innovation however how precisely is it unique, how would we arrive, by what method will it influence our lives, and all the more significantly, when will we have the option to utilize it? The fundamental differentiator somewhere in the range of 4G and 5G is limit and inactivity. These highlights are not exactly what separate the two advancements, they are the explanation we need 5G[1].

Description About how 5G technology differs from others:
5G is a not-yet-actualized remote innovation that is expected to develop 4G. It guarantees essentially quicker information rates, higher association thickness, much lower inertness, among different upgrades. 5G innovation is relied upon to be dispatched after mid-2020 yet at the same time, there is plenty of regions in existing remote frameworks that need upgrades. 5G isn’t only a stage up from 4G, it is on another level. It gives a low start to finish inactivity, the capacity to associate with a large number of gadgets on the double, and blasting quick speeds that can move to register and preparing power away from gadgets and into the organization. This implies future remote IoT gadgets can be a lot of littler, taste force, and scale quickly. 5G will likewise turn into the basic remote foundation to help self-ruling vehicles, Virtual Reality (VR)/Augmented Reality (AR) headsets, and Smart urban communities. Along these lines, it’s not simply quicker download speeds: 5G will be a distinct advantage for some, businesses including equipment items and IoT arrangements[1].
There are no benchmark guidelines that have been set for conveying the 5G convention. Yet, numerous things can be normal during its turn out. Fake Intelligence (AI) might be utilized and upgraded to give a lot quicker network right around zero idleness. IoT (Internet of Things) may turn out to be more reasonable through one touch. 1Gbps will be normal handy information rates. Different clients may move immense information in no time. This is only a projection for 5G innovation. The way to 5G will be through the development of 4G. Most telecom transporters won’t bounce straightforwardly from mid-4G frameworks to 5G, yet rather go from 4G to 4.5G to 4.5G Pro and afterward at last to 5G[1].
Drawbacks of 5G Technology:
There are many drawbacks to the 5G technologies that are to be considered.

- Obstacles can affect connectivity:
The series of 5G connectivity is not great as the rate waves are only able to travel a short reserve. The more description is that the 5G Signals can be interrupted by the physical obstacles such as trees, towers, walls, and buildings. The obstacles will also block, the telecom trade is spreading current cell fortifications to intensification the transmission reserve[1].
- Opening prices for the rollout are high:
The costs identified with the improvement of the 5G framework or transformations to the existing cell foundation will be high. This sum will be additionally exacerbated by the continuous upkeep costs expected to guarantee the fast availability, and it’s reasonable the clients will expose the brunt of these huge sticker prices. Cell administrators are hoping to limit these expenses by investigating elective choices as organization sharing[1].
- Limitations of Rural Access:
While 5G may achieve genuine availability for the dominatingly metropolitan regions, those living in the provincial settings won’t advantage from the association. The way things are, numerous distant regions countrywide can’t get to any type of cell availability. The 5G transporters will target huge urban communities with bigger populaces, in the long run working their way into the external territories, however, it’s not likely this will happen at any point shortly. Subsequently, just a portion of the populace will profit by 5G correspondence[1].
- Battery Drain by the devices:
The 5G technology uses more battery in mobile devices, the batteries are not talented to activate for an important period. The battery technology required to loan to allow for this improved connectivity where a single responsibility will power a cellphone for a full day[1].
- Upload speeds don’t match download speeds:
The download paces of 5G innovation are unfathomably high, sometimes up to 1.9Gbps. In any case, the transfer speeds are infrequently more than 100Mbps, which isn’t exactly as extraordinary as at first promoted. According to the existing portable network, in any case, the transfer speeds are higher than being seen with 4G LTE[1].
- Detracting from the Aesthetics:
The erection of more cellphone pinnacles, or expansion of existing cellphone towers, isn’t invited by most networks since they are believed to decrease the general look and feel of a territory. With 5G, there will be a requirement for expanded framework advancement, which won’t be viewed as something beneficial for neighborhood inhabitants[1].
References:
1. Protei. 23rd September 2020; Available from: http://protei.me/blog/telecom-news/the-mobile-wireless-communication-technology-journey/.
2. Silicon-press. 23rd September 2020; Available from: http://www.silicon-press.com/briefs/brief.3g/.

